ned
|
| posted on 5/8/03 at 09:38 AM |

|
|
lightweight chassis designs?
This post is purely out of curiousity, but has anyone designed/modelled a lightweight chassis?
I know we have had oversize chassis's both in terms of width, length and height, but wondered if anyone had done any analysis of the weight of
various tube sections and designs in addition to the tortional/rigidty tests that some people on here have modelled...
i would be guessing perhaps a BEC builder might have??
Ned.
beware, I've got yellow skin
|
|
|
|
|
mranlet
|
| posted on 5/8/03 at 03:35 PM |

|
|
There is a book called "Chassis Engineering" by Frank Herbert (IIRC) in which the author discusses material selection, spaceframe versus
monocoque, and methods for achieving maximum torsional stiffness (includes many pictures of wooden frame models and addresses rails-style frames,
NASCAR rollcage frames, Transmission tunnel frames, etc). I'm sure Amazon.com has it.
The similarities between the frame they construct in the book and the Locost frame are subtle but important. Their frame is also meant for filling
the body of a sportscar and accomodating a V-6 or V-8. Their frame is also made from aluminum and uses sheer panels in lieu of cross bracing in
several places (front and rear firewalls, footwells, etc).
Check it out!
-MR
|
|
|
Rob Lane
|
| posted on 5/8/03 at 04:19 PM |

|
|
Martin at MK did an ali chassis for Ron at the beginning. It was finally taken over by a guy to complete. I have some pics somewhere.
It was beautifully made and welded. You could pick it up with one finger it was so light.
Martin still has some of the special order ali box section left!
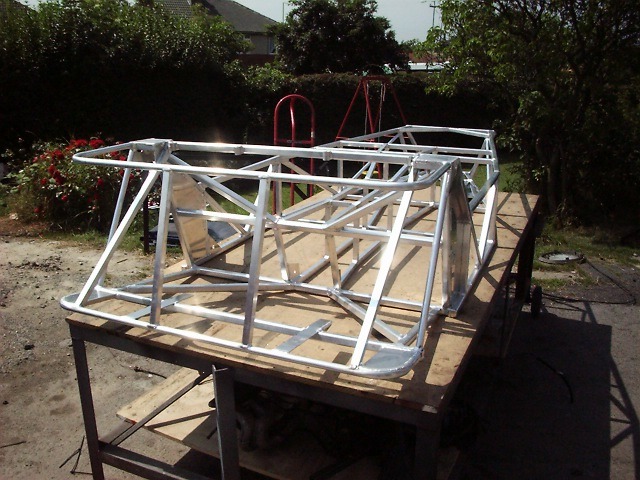
 
Rescued attachment OTHER059.jpg
|
|
|
Rob Lane
|
| posted on 5/8/03 at 04:39 PM |

|
|
This one as it appeared at Autosport Show.
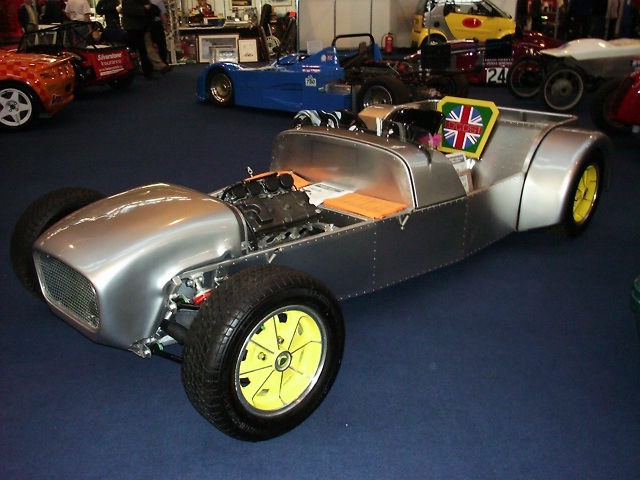
 
Rescued attachment Alicar.jpg
|
|
|
ned
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 08:34 AM |

|
|
thanks for the replies...
2 things...
firstly, i was of the impression an ally chassis was a bad thing due to fatigue of the metal etc
secondly, the blue car in the background is a vauxhall 16v engined lola, that i have driven at goodwood (136mph on limiter  ) )
Ned.
beware, I've got yellow skin
|
|
|
VinceGledhill
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 09:47 AM |

|
|
MK on their website in their FAQ
Q. Can I get an aluminium chassis?
A. No. Aluminium chassis suffer from metal fatigue which leads to premature failure. The ones that were made were for demonstration puposes only
Regards
Vince Gledhill
Time Served Auto Electrician
Lucas Leeds 1979-1983
|
|
|
DaveFJ
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 09:52 AM |

|
|
Why should metal fatigue be such a problem for a well designed chassis?
A Lynx helicopter for instance has a entirely aluminium construction and I would suggest far higher loadings combined with an enormous vibration
problem, and yet they rarely begin to show signs of failure/cracking less than 10 years from manufacture.
|
|
|
David Jenkins
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 09:58 AM |

|
|
But all helicopters get closely inspected at very regular intervals...
I doubt whether a Locost would be stripped and rebuilt after 500 hours of operation...
DJ
|
|
|
Mark Allanson
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 10:03 AM |

|
|
The lynx is a bit more complicated than a locost . EVERYTHING is structural, if we cracked one of the front screens, the aircraft was grounded until
replaced, apparently it was a significant part of the structure.
I think the stress comes into play is the chassis is not rigid, the locost chassis is definately not that rigid - try tying a piece of string, so it
is taught, from your roll bar to the front of the chassis and then jack it up.
The constant (even if small) flexing gives the aluminium a hard time and it ultimately fails
|
|
|
ned
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 10:12 AM |

|
|
thanks guys, i though tthis was the case.
just wondered if anyone had tried anything with different size tubing or tried building a 'superlight' or equilavent something
chassis....
Ned.
ps thought the BEC guys would be the ones to try it to get the power-weight ratios as good as poss..
beware, I've got yellow skin
|
|
|
DaveFJ
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 10:12 AM |

|
|
fair points and yes we definately 'over service' our military aircraft - i would be interested to know the life expectancy of an ali
chassis though....
|
|
|
Mark Allanson
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 11:03 AM |

|
|
I suppose if you honeycoombed all the appertures (except where you get in etc!) and welded ally sheet to both sides if the HC'd sections, the
chassis might be stiff enough for ally?
|
|
|
VinceGledhill
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 11:57 AM |

|
|
You could build one and then do racer type testing. In other words. Build it. Then test it until it breaks. Fix it at that point and make it
stronger. Test it again until it breaks.... Fix it at that point and make it stronger.
Etc Etc until it doesn't break anymore. Draw plans of what you have.... Now we have a lightweight aluminium one that doesn't break....
Regards
Vince Gledhill
Time Served Auto Electrician
Lucas Leeds 1979-1983
|
|
|
ned
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 12:08 PM |

|
|
quote:
Originally posted by VinceGledhill
You could build one and then do racer type testing. In other words. Build it. Then test it until it breaks. Fix it at that point and make it
stronger. Test it again until it breaks.... Fix it at that point and make it stronger.
Etc Etc until it doesn't break anymore.
oh yeah i can just imagine, racing along [something breaks] backwards in to nearest wall, tyre wall, tree, bush or other car, chassis is so mangled
you'd have to start again from scratch and would be lucky to find the failure point and sufficiently strengthen and rebuild it, assuming the
driver is unhurt....

Ned.
[Edited on 6/8/03 by ned]
beware, I've got yellow skin
|
|
|
Rob Lane
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 12:30 PM |

|
|
No, the real truth is Martin just can't be bothered to make them due to the extreme hassle he had from some customers. It was during his
earlier times when he had hassle from Ron etc. to contend with as well. Sort of put him off further developement.
The chassis is not easy to make in ali, it takes three times longer to make and a true finished cost for chassis alone would have been £2500.
The chassis as shown in pic was not fully completed and had further stiffening done to it later. I just happened to be there when the table was
wheeled out.
Martin had sussed the design out OK and done other things but in the overall scheme of things the chassis life was limited. Especially if exposed to
any salt water as in Sept roads when morning de-icing is done.
When I win the lottery (names on one somewhere!) it's either spend a fortune with MK as single commission build or go for a R500.
Actually went down to Caterham Midlands last week to ogle at the Porsche Silver R500 that's in just now. Just toooo damn pricy!
|
|
|
Rob Lane
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 12:41 PM |

|
|
Found this detail of one of the welds. It's so beautiful a weld in ali.
The square tube was special order and he had to take about 500kg of the stuff.
I have other pics but no point posting them all.
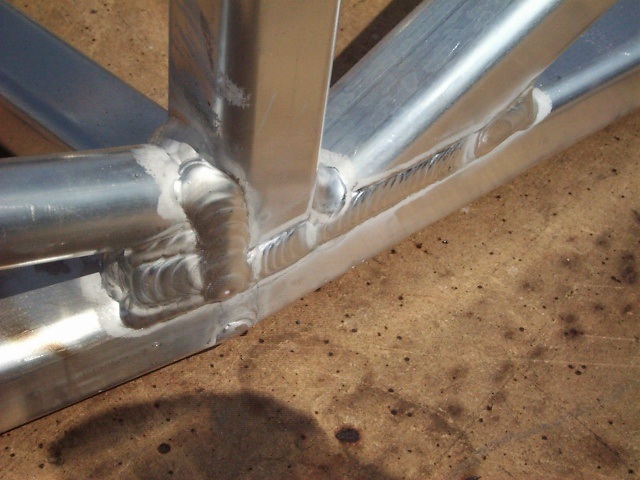
 
Rescued attachment OTHER021.jpg
|
|
|
VinceGledhill
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 12:41 PM |

|
|
Ned. That's how they tested the cobras prior to le-mans. Don't believe me then take a look at Cobra Farari wars. On BBC4 quite a bit.
Regards
Vince Gledhill
Time Served Auto Electrician
Lucas Leeds 1979-1983
|
|
|
stephen_gusterson
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 07:44 PM |

|
|
Ned
See one of the posts in pet peeves.
the chassis is pretty minimal already......
  
atb
steve
|
|
|
chrisg
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 08:19 PM |

|
|
Some of the hillclimb boys use ali chassis but they are"lifed" and only expected to last a certain amount of time, no good on a road car,
unless you plan to keep changing the chassis!
Cheers
Chris
[Edited on 6/8/03 by chrisg]
Note to all: I really don't know when to leave well alone. I tried to get clever with the mods, then when they gave me a lifeline to see the
error of my ways, I tried to incite more trouble via u2u. So now I'm banned, never to return again. They should have done it years ago!
|
|
|
cymtriks
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 08:26 PM |

|
|
lightweight
Some thoughts..
Aluminium is no lighter than steel for a properly designed spaceframe. Yes, it is one third of the weight but it also one third of the stiffness and
is much more prone to suffer from fatigue. In order to restore the stiffness in a true spaceframe you will then need to tripple the tube weight which
brings the weight of the chassis back to where you started.
Audi and others have made what they call spaceframe chassis. These mass produced cars are actually much closer to ladder frames in concept.
The Lotus Elise chassis is light weight, stiff and made of aluminium. It exploits the big tube principle of chassis design. Basically tube stiffness,
for a given wall thickness, goes up as the cube of the tube size. So double the diameter and you have eight times the stiffness. Make tubes as big as
those down the sides of the elise and you get high stiffness for very little weight. The elise chassis can be regarded as a very clever ladder
frame.
For ladder frames big tubes with thin walls are better but for spaceframes it's usually the triangulation that counts. Theoretically it's
all that counts. The book lowcost chassis is about equal to a decent ladder frame and there are much worse spaceframes on the market. Most kitcar
chassis spaceframes are not properly triangulated. In most cases it really is that simple.
The easiest way to reduce the weight of the lowcost is to reduce the floor, tunnel and footwell thickness from the book 16g down to 20g (1.0mm) sheet.
This has a very small effect on chassis stiffness but saves an estimated 30lbs / 14Kg.
In my pictures section I've posted a design for a high stiffness lowcost chassis. There is extra triangulation around the front suspension and
tube R is replaced by two Y braces. To save weight the 3/4 inch tubes in the tunnel can be deleted. Leave the arch over tube B to help support the
gear lever and handbrake mount though. Panel the tunnel in on the top sides and bottom to make it into a welded steel tube.
Those mods will bring the book chassis up from about 1200ftlbs per degree of twist to about 2700. Scroll backwards on this forum and you'll find
my posts decribing this in more detail.
The double Y brace across the engine bay top is better than one long diagonal and is much better than the two short doagonals used on some seven type
chassis.
I hope this is of interest!
|
|
|
DaveFJ
|
| posted on 6/8/03 at 10:14 PM |

|
|
I'm intrigued (purely academically) wether the use of tesioned wire cross braces could be used to replace some of the cross bracing and save
weight ?
|
|
|
Spyderman
|
| posted on 7/8/03 at 12:18 AM |

|
|
quote:
Originally posted by protofj
I'm intrigued (purely academically) wether the use of tesioned wire cross braces could be used to replace some of the cross bracing and save
weight ?
It was successfully used in aircraft!
I suppose the biggest problem would be the tensioning. Cost wise it must work out cheaper and/or easier to weld more solid members in.
Terry
 
Spyderman
|
|
|
Rorty
|
| posted on 7/8/03 at 01:23 AM |

|
|
cymtricks:
quote:
In order to restore the stiffness in a true spaceframe you will then need to tripple the tube weight which brings the weight of the chassis back to
where you started.
I don't agree. I've used aluminium for a miriad of structures purely for the weight savings over their (tested) steel
counterparts.
With regards to an aluminium chassis, the structure must be really rigid. Any flexion will result in failed members and welds.
I've seen a lot of motorbike frames brought in for repairs. It's never the main frame (with normal usage), but the flimsier, bolt-on rear
subframes that frequently flex under the rider's bum, that ultimately fail.

Cheers, Rorty.
"Faster than a speeding Pullet".
PLEASE DON'T U2U ME IF YOU WANT A QUICK RESPONSE. TRY EMAILING ME INSTEAD!
|
|
|
mranlet
|
| posted on 7/8/03 at 02:04 PM |

|
|
As far as I know, aluminum can vary greatly...
T-16 will give you different results than high-grade aircraft Aluminum. The weight also varies greatly, people have claimed that Aluminum is 30% the
weight of steel, which may be true of some forms, but the aluminum you would need for the rigidity (given that the design is minimally modified) would
be more like 60% of the weight of steel. There are also composite aluminum materials, such as AMMC, which use are a synthesis of fiberous ceramics
and aluminum. These materials exceed the torsional strength of an equal steel beam and are roughly 65% of the weight f steel. The only applicatoins
that I know of for AMMS are in the engine-to-differential torque tube in late model Corvettes and in the housing of some turbojet aircraft engines.
The Chassis Engineering book to which I refered to earlier has a frame constructed of 2"x2" RHC aluminum with a 1/10" beam
thickness. Their frame is approximated at 200-250lbs at a size that would fit within a late 80's Camaro and is designed to accomodate a V-8.
The author points out that the use of aluminum will save you weight, but the durability is only practical for a race car that will only see one or two
years of use and could be hazardous for a street-driven car.
The torsional stiffness of the frame in Chassis Engineering is worked out to be something along the lines of 8000lb/deg IIRC... The Locost frame as
depicted in the book is only about 1200lb/deg. For further comparison, and a Mazda Miata is around 3800lb/deg, A Lotus Elise is 8000lb/deg, and a
McLaren F1 can take 25,000lb/deg. (http://www.ultimav12.ca/chassis/ - a wonderful site that depicts frame improvements on an Ultima GT-R)
I've designed my frame with 2"x2"x.1" RHS steel (since it's cheap and readily available) and 18ga sheer panels. My
frame also employs a quadrilateral transmission tunnel that is 12" tall, 18" wide at the base and 12" wide at the crest with sheer
panels on the top 3 sides to serve as scatterguard and crossbracing underneath (which could be removed in the event of major transmission and
driveshaft work). I tried to provide triangulation in every area that needed it and eliminated members that did not give substantial gain. I also
joined some 2"x2" sections of RHS to make 2"x4" beams for high stress areas like the crosspieces at the front and rear
suspension. This semi-monocoque frame should yeild a theoretical 6500-7000lb/deg.
Anyway, not to get too far off topic - I understand the point about wanting to see how lightweight frames effect performance, but it has pretty well
been determined that an aluminum frame would be costly and difficult to adapt for a street vehicle.
A: The benefits of lightweight materials depend greatly on your application.
Is isn't about more metal, it's about where you put it. I hope this helps.
-MR
[Edited on 7/8/03 by mranlet]
|
|
|
ned
|
| posted on 7/8/03 at 02:31 PM |

|
|
not to detract from anyones ally discussions, though my original question should have been along the lines of lightweight chassis in steel!
as has been said in the peeves and rants section i wouldn't have the first clue or skills to weld anything other than mild steel!
I was just curious as I know (have seen chassis' at show's) that caterham use some small diameter tube (presumably in tension) on their
superlight chassis and wondered if anyone had substituted this on a book or near book/modified chassis...
I guess the answer would be that you loose torsional rigidity unless adding more bracing/structural members as per cymtriks mods...
thanks,
Ned.
beware, I've got yellow skin
|
|
|